


Medically Reviewed By Margaret Etudo. Written By The Vitamins For Woman Team.
Niacinamide for acne scars and eczema is a widely accepted treatment. The compound is found in various skincare products, including moisturizers and serums. Read on to learn its benefits and how to use it.
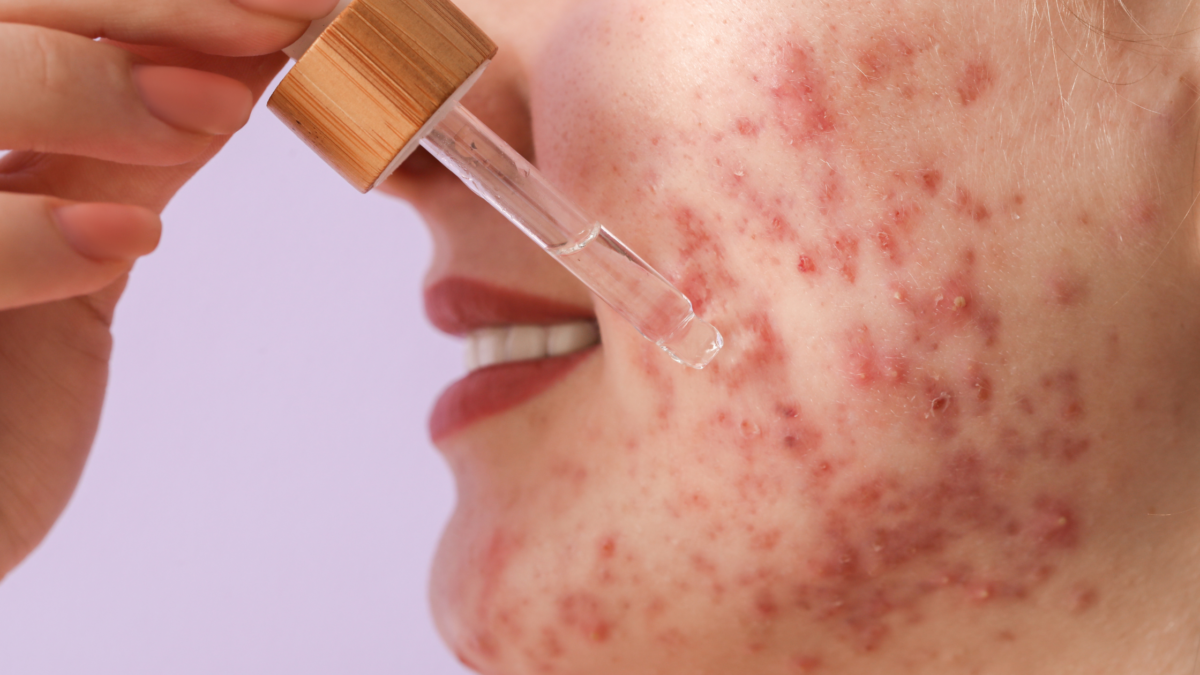

medically reviewed by margaret etudo, BPharm. written by the vitamins for woman team.
Niacinamide, a form of Vitamin B3, has been widely accepted as an essential nutrient for the body and skin in particular, so you will likely find it in many skincare products. Niacinamide helps produce ceramides, compounds that help improve skin moisture and protect the skin barrier against environmental damage.
Its anti-aging and inflammation-reduction properties also make it an accepted treatment for acne, scars, and fine line reduction. Besides these benefits, niacinamide helps regulate oil production, making it easier to prevent skin clogging and acne.
With the various benefits of niacinamide for acne scars and eczema, the question is, how does it work, and where else can you get it apart from in your skincare products?
If you have ever confused Niacin and Niacinamide, you are not alone. In fact, the similarities in their names cause most people to mistake them as one and the same at first glance. However, they differ greatly, and you need to look closely to avoid selecting the wrong compound for various tasks.
We have a table below detailing the differences in the structure, uses, and effects of Niacin and Niacinamide.
|
Niacin |
Niacinamide |
|
|
Other Name |
Nicotinic Acid |
Nicotinamide |
|
Chemical Structures |
It has a carboxyl group attached to its ring structure. |
It lacks a carboxyl group and instead has an amide group. |
|
Primary Uses |
It is commonly used to lower cholesterol and improve heart health. |
Used in skincare to improve skin health by reducing inflammation, hyperpigmentation, and signs of aging. |
|
Effects on Body |
It converts into niacinamide in the body, but in high doses, it works directly to lower LDL (bad cholesterol) and raise HDL (good cholesterol). |
Does not have the same cholesterol-lowering effects as niacin but is more focused on energy metabolism and maintaining healthy cells, especially in the skin and immune system. |
|
Side Effects |
High doses can lead to side effects like flushing, liver toxicity, and stomach upset. |
Generally well-tolerated, with fewer side effects, even at high doses. |
Essentially, niacinamide is derived from niacin, and they both have different uses, side effects, and components.
Niacinamide is a common treatment for acne because of its several benefits for acne treatment. They include:
You may be familiar with skincare products that contain niacinamide. However, skin products are not the only sources of niacinamide. Like every other vitamin, you can get niacinamides from food and supplements.
There is an ongoing debate regarding whether skin products, foods, or supplements are the best sources of niacinamide for acne scars. No one answer fits all. So, we will discuss each and list their pros and cons for easier comparison.
Skin products like creams and balms are common sources of niacinamides. They must be applied topically and are better for targeted skin benefits like acne removal and improving skin texture.
Pros
Cons
You can also get niacinamide from foods since it is a form of vitamin B. Foods like eggs, beans, fish, etc. are good sources of niacinamide.
Pros
Cons
So, for maximum benefits, consider combining skin products containing niacinamide with foods and supplements. Check your intake to ensure you are not exceeding the compound’s RDA.
Like every other vitamin, you can get Vitamin B3 from various food sources. These include:
Eggs contain around 2% of the recommended daily intake of niacin. It also provides other nutrients like protein, vitamins B12 and D, and minerals like selenium and choline.
Cereals, particularly whole grains, are essential sources of Vitamin B3. For instance, a cooked cup of oatmeal can contain about 12% of the RDA for niacin. Therefore, you can maintain an optimal level of Vitamin B3 by consuming enough cereals.
Green veggies like spinach, kale, and broccoli contain niacin in smaller amounts than other sources. For instance, you can only get around 5% of your RDA niacin from a cup of cooked spinach. However, they also reduce inflammation, support the immune system, and provide other essential nutrients.
Various beans, such as kidney beans, black beans, and chickpeas, contain good Vitamin B3. Up to 6% of the RDA of niacin can be obtained from a cup of cooked black beans. The niacin in beans supports metabolism, energy production, and healthy skin.
Fatty fish is one of the best sources of Vitamin B3. For example, a 3-ounce serving of cooked tuna can give you half the RDA of niacinamide as an adult. These fish also contain Omega-3 fatty acids, which are good for the brain and heart.
Milk and other dairy products are also good sources of Vitamin B3. A cup of whole milk provides about 2% of your RDA for niacin. Milk also contains other nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
Getting a suitable and effective niacinamide product involves considering a variety of factors. These include:
While you want the niacinamide to work quickly and improve your skin, taking it in larger concentrations can be detrimental. Instead, choose products with 2% to 10% for the best result, depending on your individual needs.
Niacinamide skin products come in various formulations, including creams, serums, toners, masks, and moisturizers. Choose the formulation that best suits your needs. For instance, moisturizers are great if you want to incorporate niacinamide into your daily skincare routine.
Check the ingredient list and make sure you choose a niacinamide product that does not contain ingredients that you are allergic or sensitive to. Also, check for additional ingredients that may be beneficial to your body.
Choose niacinamide products with a pH balance of around 5.0 to 7.0 because niacinamide works best in slightly acidic or neutral pH levels.
There are various niacinamide requirements for various skin types. If you have oily skin, look for gel-based or lightweight serums. If you have dry or sensitive skin, select products with added hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid or ceramides. A balanced formula works better for combination skin.
While these are major considerations that can directly affect your skin when using a niacinamide product, you should also consider the brand you’re buying from, packaging, price, and value.
Yes, niacinamide is versatile enough to combine with other active and hydrating ingredients. These include hyaluronic acid, retinol, vitamin C, salicylic acid (BHA), AHAs (glycolic acid, lactic acid), ceramides, and peptides.
Although niacinamide is great and has various benefits, it also has some side effects, including nausea and mild irritation. Severe side effects may reduce the overall benefits in the long run, so you must know how to avoid them. Simply do the following to take niacinamide without side effects:
You will likely have expectations before you start taking niacinamide. This is great, especially since you may have been told generally that it will improve your skiing and clear your acne.
However, you deserve to know more, so we will spell out the possible effects of niacinamide intake for you. They include:
Yes, niacinamide is good and safe for sensitive skin. It is gentle on the skin and has hydrating properties. Niacinamide also reduces skin sensitivity by strengthening the skin barrier. Furthermore, when used right, it helps to calm and soothe the skin.
Yes, you should use niacinamide for inflammatory acne. The compound has anti-inflammatory properties that make it suitable for managing such conditions. It can also regulate sebum production, reducing acne flare-ups. To use niacinamide in controlling your acne, you should choose the right quantity and introduce it gradually into your skincare routine.
Yes, you can use niacinamide with eczema. In fact, it can be great for eczema-prone skin due to its soothing, anti-inflammatory, and barrier-strengthening properties. Niacinamide will strengthen your skin barrier, prevent moisture loss, and reduce eczema triggers.
Niacinamide stands out as a major ingredient in various skincare products due to its healing properties. Whether you’re looking to target acne, reduce the appearance of scars, or soothe eczema-prone skin, niacinamide offers a gentle yet powerful solution. Remember to choose products tailored to your skin type, start with a lower concentration, and consult with a dermatologist if needed. With consistent use, you can achieve a healthier, more radiant complexion.
NIACINAMIDE: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews. (n.d.). https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1534/niacinamide
Unlocking the potential of niacinamide: What percentage is effective for skin health? Curology. https://curology.com/blog/niacinamide/#:~:text=A%205%25%20concentration%20of%20niacinamide%20has%20been%20shown%20to%20be,re%20new%20to%20using%20niacinamide
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
[…] acne scars, like ice pick, boxcar, and rolling scars, are atrophic, meaning they form from chronic […]